Table of Contents
Raising women's participation in the labor force to the same level as men can boost India's GDP by 27 percent.
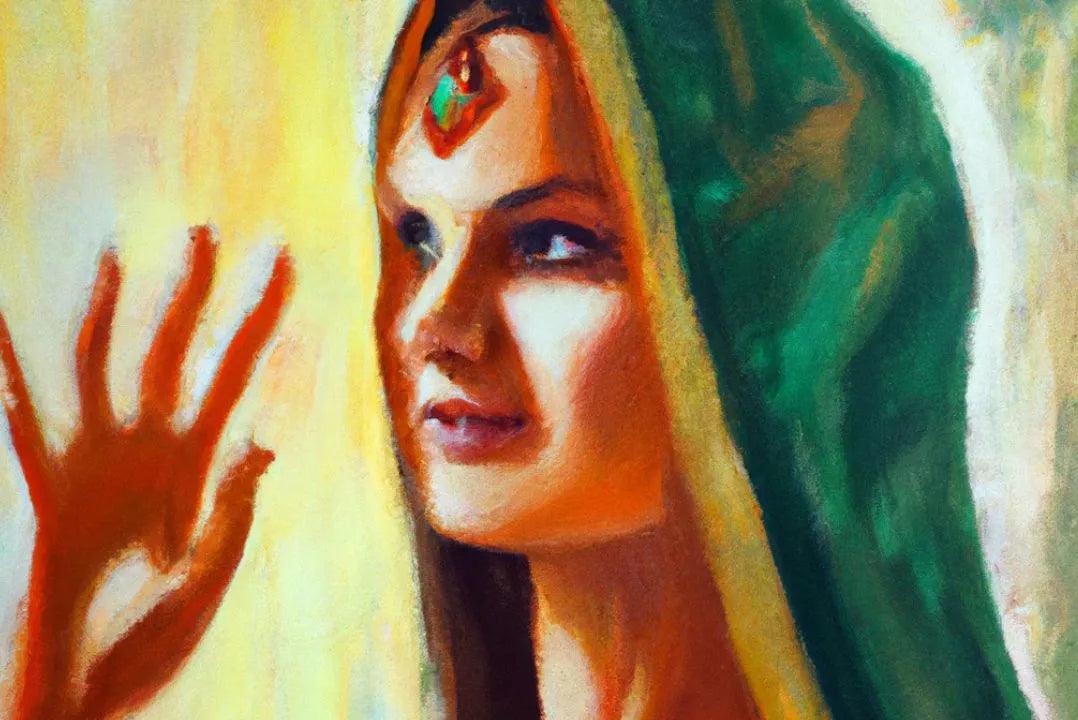
India has one of the world's largest populations, and women's role in its workforce is important. In recent years, women's participation in the Indian workforce has increased, but there is still a long way to go to achieve gender equality in the workplace.
Women face several challenges, including low levels of participation, discrimination, and unequal pay. The participation of women in the Indian workforce has increased over the years, but it remains low compared to other countries. According to the World Bank, India's female labor force participation rate was 24.8% in 2019, compared to the global average of 48.9%.
One significant barrier for women in the Indian workforce is the lack of access to education and training opportunities. Many women cannot access higher education or vocational training, which limits their ability to secure well-paying jobs. Another key reason for the low participation of women is the prevalence of gender stereotypes and discrimination. Many face societal pressure to prioritize domestic responsibilities over paid work.
Discrimination and unequal pay are also significant issues. Women are often paid less than men for the same work and are often relegated to lower-paying, low-skilled jobs. Additionally, they may face discrimination and harassment in the workplace, which can create a hostile and unwelcoming environment.
Despite these challenges, women in India have made significant strides in recent years. The government has implemented several policies and initiatives to promote gender equality and increase participation. These include the implementation of the National Policy for the Empowerment of Women, introducing affirmative action policies, and establishing women-centric programs and initiatives such as the Mahila Udyam Nidhi Scheme. Indidha is one such startup launched by Priyanka Singh. There has been a growing recognition of the importance of gender equality in the workforce, which has led to increased awareness and efforts to address these issues.
While women's participation in the Indian workforce has increased, much work remains to be done, and this includes addressing the root causes of gender discrimination. According to World Bank, India's female labor force participation rate was 27.2% in 2019, compared to 82.7% for men.
There is still a long way to go in achieving gender equality in the workplace. The government and other stakeholders must continue implementing policies and initiatives to support and empower women in the workforce.